Tutorial section - SMS
Send SMS with SMPP using Java
Sending SMS with the SMPP API using the Java programming languageRelated
SMPP RouterSMPP Load Balancer
SMPP Load Test tool
SMSC Simulator
SMPP SMS Gateway platform
Tyr SMS Gateway
SMS Code Bench
The jSMPP library can be used to build an SMPP client that can make SMPP requests using Java. This library's higher-level functions can be used to synchronously submit SMS to an SMS gateway or SMSC.
SMPP requirements and resources
SMPP is the Short Message Peer-to-Peer protocol and is used by applications for sending and receiving SMS. An SMPP client can be used to connect to an SMSC or SMS gateway using the SMPP protocol. An SMPP account, including special Developer accounts, can quickly and easily be obtained for using the Melrose Labs Tyr SMS Gateway or SMSC Simulator. The following are required to send SMS with SMPP:
- SMPP Protocol [reference]
Short Message Peer-to-Peer Protocol v3.3, v3.4 and v5 specifications and guides - SMPP Client [tool]
Browser-based SMPP client supporting SMPP v3.x and v5 via Web Sockets
Java requirements and resources
Java is a programming language and can be used to quickly and easily add SMS support for programmatically sending and receiving SMS messages. Use it for transactional messaging and notifications between your application and mobiles. The following are required to send SMS using Java:
- Java
Java programming language
Requirements and resources
The following are required to send SMS with SMPP using Java:
- jSMPP
jSMPP Java Library
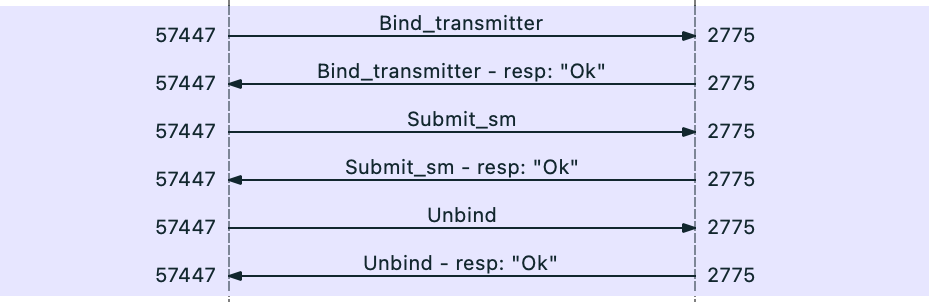
SMPP Flow
The code connects to the server, then establishes an SMPP transmitter bind by sending a bind_transmitter SMPP PDU. It receives a bind_transmitter - resp with a positive "Ok" acknowledgement.
A submit_sm PDU is then sent by the code to send the message. The message ID for the submission is returned in the submit_sm - resp.
The session is then closed by the code sending an unbind PDU, which is acknowledged with a unbind - resp. The TCP session is then closed.
Code
Create the file SimpleSubmitExample.java containing the code below. Replace the hostname smscsim.smpp.org, port 2775, SYSTEMID and PASSWORD values with those for the SMPP API account from your provider. Alternatively, use SMPP credentials for the Melrose Labs SMSC Simulator or the smpp.org SMSC simulator.
The following example Java code opens an SMPP transmitter bind to smscsim.smpp.org on port 2775 (SMPP port), and then sends the message Hello World #$£ to mobile number 447712345678 from the source/sender address MelroseLabs. The message ID in messageId is that returned from smscsim.smpp.org after a successful submission. The SMPP system ID and password for the SMPP account are contained in SYSTEMID and PASSWORD.
SimpleSubmitExample.java
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
import org.jsmpp.InvalidResponseException;
import org.jsmpp.PDUException;
import org.jsmpp.bean.Alphabet;
import org.jsmpp.bean.BindType;
import org.jsmpp.bean.ESMClass;
import org.jsmpp.bean.GeneralDataCoding;
import org.jsmpp.bean.MessageClass;
import org.jsmpp.bean.NumberingPlanIndicator;
import org.jsmpp.bean.RegisteredDelivery;
import org.jsmpp.bean.SMSCDeliveryReceipt;
import org.jsmpp.bean.TypeOfNumber;
import org.jsmpp.extra.NegativeResponseException;
import org.jsmpp.extra.ResponseTimeoutException;
import org.jsmpp.session.BindParameter;
import org.jsmpp.session.SMPPSession;
import org.jsmpp.session.SubmitSmResult;
import org.jsmpp.util.AbsoluteTimeFormatter;
import org.jsmpp.util.TimeFormatter;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class SimpleSubmitExample {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SimpleSubmitExample.class);
private static final TimeFormatter TIME_FORMATTER = new AbsoluteTimeFormatter();
public static void main(String[] args) {
SMPPSession session = new SMPPSession();
try {
log.info("Connecting");
String systemId = session.connectAndBind("smscsim.smpp.org", 2775,
new BindParameter(BindType.BIND_TX,
"SYSTEMID", "PASSWORD", "",
TypeOfNumber.UNKNOWN, NumberingPlanIndicator.UNKNOWN, null));
log.info("SMSC system ID is {}", systemId);
try {
SubmitSmResult submitSmResult = session.submitShortMessage("",
TypeOfNumber.UNKNOWN, NumberingPlanIndicator.UNKNOWN, "MelroseLabs",
TypeOfNumber.INTERNATIONAL, NumberingPlanIndicator.UNKNOWN, "447712345678",
new ESMClass(), (byte)0, (byte)1, null, null,
new RegisteredDelivery(SMSCDeliveryReceipt.DEFAULT),
(byte)0,
new GeneralDataCoding(Alphabet.ALPHA_DEFAULT, MessageClass.CLASS1, false), (byte)0,
"Hello World €$£".getBytes());
String messageId = submitSmResult.getMessageId();
log.info("Message successfully submitted (message_id={})", messageId);
} catch (PDUException e) {
// Invalid PDU parameter
log.error("Invalid PDU parameter", e);
} catch (ResponseTimeoutException e) {
// Response timeout
log.error("Response timeout", e);
} catch (InvalidResponseException e) {
// Invalid response
log.error("Receive invalid response", e);
} catch (NegativeResponseException e) {
// Receiving negative response (non-zero command_status)
log.error("Receive negative response", e);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("IO error occured", e);
}
session.unbindAndClose();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Failed connect and bind to SMSC", e);
}
}
}
Run SimpleSubmitExample.java:
% java -cp jsmpp-3.0.0.jar:slf4j-simple-2.0.6.jar:slf4j-api-2.0.6.jar SimpleSubmitExample.java
[main] INFO SimpleSubmitExample - Connecting
[main] INFO org.jsmpp.session.SMPPSession - Connected from port 50897 to smscsim.smpp.org/34.242.18.250:2775
[PDUReaderWorker-7f40fb0a] INFO org.jsmpp.session.SMPPSession - Starting PDUReaderWorker
[main] INFO org.jsmpp.session.SMPPSession - Other side reports SMPP interface version 34
[main] INFO SimpleSubmitExample - SMSC system ID is MelroseLabsSMSC
[main] INFO SimpleSubmitExample - Message successfully submitted (message_id=0ac4b64e8f54fa45f4dc2cf7a070bb520d9f)
[PDUReaderWorker-7f40fb0a] INFO org.jsmpp.session.SMPPSession - Reading PDU session 7f40fb0a in state CLOSED: Socket closed
The above shows a connection being made to smscsim.smpp.org on port 2775 and an SMPP transmitter bind (BindType.BIND_TX) being established using the SMPP system ID "SYSTEMID" and password "PASSWORD".
A message is then submitted to the SMSC/SMS gateway using session.submitShortMessage() (sends an SMPP submit_sm PDU), and a response (submit_sm_resp PDU) is received from the SMSC/SMS gateway with the message ID for the submitted message (message_id=0ac4b64e8f54fa45f4dc2cf7a070bb520d9f).
Using in production
Whatever the language or API, you can send SMS and receive SMS between applications and mobiles for a wide range of uses with any of the trusted and reliable CPaaS services from Melrose Labs. Take a look at our Messaging, SMS gateway and Bulk SMS solutions, and sign-up for a Developer account on our Tyr SMS Gateway service to try us out.
We provide a wide range of CPaaS services and infrastructure to organisations, including cloud platforms that enable you to run your own SMS gateway.
Get in contact with us to find out more about CPaaS voice, messaging, video and identity from Melrose Labs.
Testing
For testing your application's SMS support when using the SMPP protocol, we recommend starting with the Melrose Labs SMSC Simulator service to simulate SMS message delivery to mobiles (MT SMS) and simulate SMS messages from mobiles (MO SMS). The SMSC Simulator supports SMPP v3.3, v3.4 and v5.
SMSC SimulatorFor live testing and delivery to mobiles, use the reliable and dependable Melrose Labs Tyr SMS Gateway for A2P, P2A, bulk, wholesale and business SMS, text marketing and other uses. The Melrose Labs Tyr SMS Gateway supports REST and SMPP APIs.
Tyr SMS GatewayAlternative APIs and languages
Other APIs covered in our tutorials that can be used for sending and receiving SMS using Java include: REST
Other languages covered in our tutorials that can be used for sending and receiving SMS with SMPP include: Python, PHP, C++, C#, Perl, Go, Node.js, Ruby
